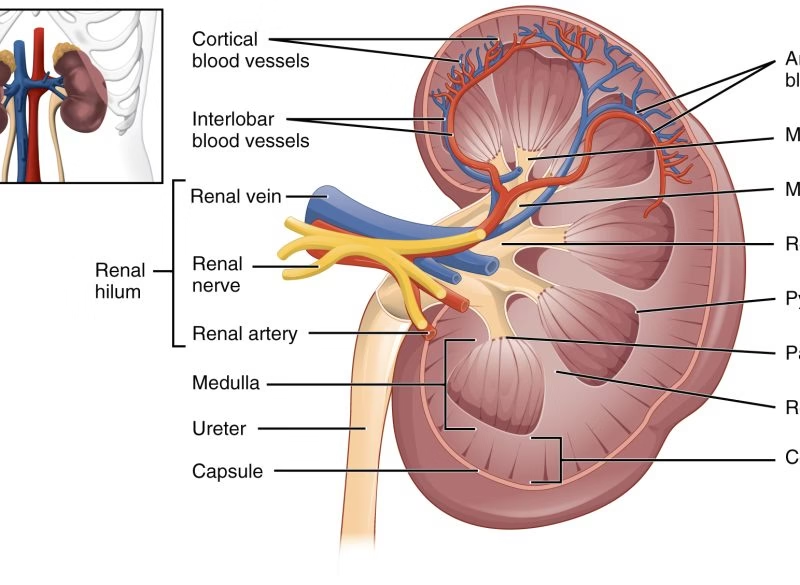
While UTIs (Urinary Tract Infections) are often thought of as a “women’s health issue,” they can also affect men—and when they do, they can be particularly serious. A UTI occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract, leading to infection in parts such as the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. In men, UTIs tend to be less common but may present with more complicated symptoms and require careful medical attention.
Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, knowing your risk factors, and adopting proper prevention strategies is essential for maintaining a healthy urinary tract and avoiding recurrent infections.
✅ What Is a UTI?
A UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) occurs when bacteria, often from the digestive tract, enter the urinary tract, which includes the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. In men, this can lead to:
- Bladder infection (Cystitis)
- Urethritis (infection of the urethra)
- Prostatitis (infection of the prostate gland)
Left untreated, UTIs in men may lead to more serious complications like kidney infections.
⚡ Common Causes of UTI in Men
- Bacterial infection: Escherichia coli (E. coli) from the digestive tract is the most common culprit.
- Enlarged prostate: Can block the flow of urine, allowing bacteria to grow.
- Urinary catheter use: Increases risk of introducing bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Unprotected sex: May introduce bacteria into the urethra.
- Poor hygiene: Increases chances of bacterial entry.
-
Underlying medical conditions: Diabetes or kidney stones increase UTI risk.
🚨 UTI Symptoms in Men
Identifying uti symptoms early is key to preventing complications:
- Frequent urge to urinate but passing only small amounts of urine.
- Burning sensation during urination (uti pain).
- Cloudy, strong-smelling, or bloody urine.
- Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis.
- Fever or chills (may indicate infection spreading to the kidneys).
- Discomfort in the perineal area (between the anus and genitals).
💡 Note: Some men may experience asymptomatic UTI, where infection exists but no clear symptoms are present.
⚠️ UTI Signs vs. Other Conditions
It’s important to distinguish UTI from other similar issues:
- Bladder infection: Primarily causes lower abdominal pain and frequent urination.
- Water infection (colloquial for UTI): Essentially refers to the same condition.
- Prostatitis: May include fever, perineal pain, and painful ejaculation.
- UTI symptoms female: Typically more frequent and easier to detect due to anatomical differences.
🔍 Risk Factors Specific to Men
- Age: Older men (over 50) are at higher risk, especially due to prostate enlargement.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Can cause urethritis leading to UTI.
- Medical devices: Long-term catheter use increases bacterial entry risk.
- Weakened immune system: Increases vulnerability to infections.
- Dehydration and poor hygiene: Can exacerbate the problem.
🌿 Prevention Tips for UTI in Men
- ✅ Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract. - ✅ Practice Good Hygiene
Wash the genital area regularly, and after sex, urinate to help expel any bacteria. - ✅ Safe Sexual Practices
Use protection and ensure both partners are clean to reduce infection risk. - ✅ Manage Medical Conditions
Keep diabetes and other conditions well-controlled. - ✅ Avoid Holding Urine
Empty your bladder when you feel the need, rather than holding it in. - ✅ Cranberry Products
While evidence is mixed, cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent bacterial adhesion in the urinary tract. - ✅ Probiotics
Probiotics support the health of the urinary and digestive tracts by maintaining good bacteria. - ✅ Home Remedies for Burning Urine
- Baking soda dissolved in water (under doctor’s guidance)
- Chamomile tea for its anti-inflammatory properties
⚠️ However, home remedies are not a replacement for medical treatment.
💊 Medical Treatment Options
For confirmed UTI cases, doctors typically prescribe uti tablets (antibiotics) such as:
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
- Ciprofloxacin
- Nitrofurantoin
Treatment duration depends on the severity and location of the infection. Chronic or complicated cases may require longer courses or combination therapy.
🌟 Final Thoughts
Although UTIs in men are less common than in women, they are often more serious. Being aware of the uti signs and symptoms, understanding your uti causes, and taking preventive steps can dramatically improve your urinary health.
If you experience persistent pain, burning during urination, or unusual urinary patterns, consult a healthcare professional early. Don’t ignore your urinary tract health — prevention and early treatment are always the best strategies.
👉 Take action today for a healthier tomorrow.