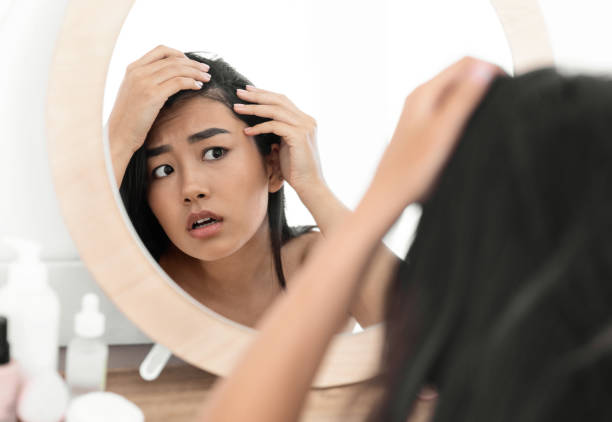
Our hair is often a reflection of our identity and can greatly influence how confident and self-assured we feel. When hair begins to fall out suddenly or in unusual patterns, it can be emotionally distressing. One of the most common yet often misunderstood conditions causing unexpected hair loss is alopecia areata—an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, resulting in patchy hair loss occurring on the scalp or various parts of the body.
Let’s explore what alopecia is, what causes it, and what you can do about it.
What Is Alopecia Areata?
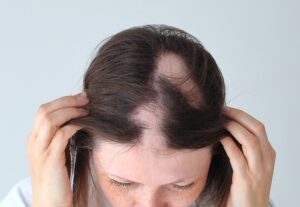
Alopecia areata is a chronic condition that causes hair to fall out in small, round patches. It can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background, though it often begins before the age of 30. In some cases, the condition remains mild and goes into remission; in others, it progresses and results in more extensive hair loss across the body.
There are different types of alopecia, depending on the areas affected:
- Alopecia totalis: Complete loss of hair from the entire scalp
- Alopecia universalis: Complete hair loss across the whole body
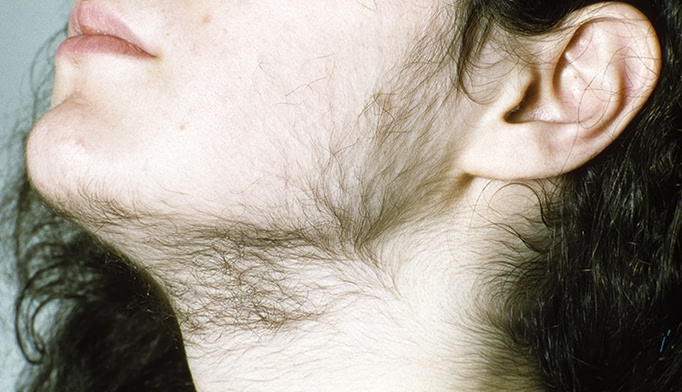
- Alopecia barbae: Hair loss specifically affecting the beard area in men
While alopecia areata does not cause physical pain or illness, the emotional toll can be significant. Understanding the nature of the condition can help individuals make informed choices about how to manage it.
Common Hair Loss Causes
Hair loss isn’t always related to alopecia. In fact, several factors can contribute to thinning hair or bald patches:
- Genetics: Inherited hair loss, often referred to as pattern baldness, is among the most frequent causes of hair shedding.
- Hormonal imbalances: Conditions like thyroid disorders, pregnancy, and menopause can trigger noticeable hair loss.
- Nutritional deficiencies: A lack of iron, vitamin D, or protein can impact hair health.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can push hair follicles into a resting phase, leading to temporary shedding.
- Medical conditions: Autoimmune disorders, anemia, and skin diseases like psoriasis can all affect the scalp.
Identifying the root cause is crucial before starting any hair loss treatment, as the approach may vary based on the underlying issue.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
If you’re noticing more strands in your brush or round patches of baldness, especially on your scalp or beard, you may be dealing with a form of alopecia. Some common signs include:
- Round, smooth patches of hair loss
- Sensation of tingling or itchiness in the area experiencing hair loss
- Thinning or brittle nails (sometimes seen with autoimmune disorders)
- New hair initially growing back as white or gray strands
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing progression and promoting regrowth.
Hair Loss Treatment Options
Though there is no definitive cure for alopecia areata, various treatments are available to help reduce inflammation, encourage regrowth, or mask the effects of hair loss.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Creams or ointments can reduce immune activity at the follicle.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This over-the-counter product helps stimulate hair regrowth.
- Anthralin: A thick, tar-like cream applied to the scalp that causes mild skin irritation to stimulate hair regrowth.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: A newer method that involves injecting platelets from your own blood into the scalp to stimulate follicles.
- Immunotherapy: Used in severe cases, this involves chemicals that trigger an allergic reaction to reset the immune response.
Each case of alopecia is unique. Some people experience spontaneous alopecia hair growth, while others may need long-term treatments or lifestyle changes to see improvements.
Hair Thinning Treatment for Females
Hair thinning in women often has hormonal or nutritional roots, making it different from male-pattern baldness. Treatments for women must be approached delicately, especially during pregnancy or menopause. Options include:
- Hormone therapy (if due to imbalance)
- Low-level laser therapy to stimulate follicles
- Biotin or iron supplements (if deficient)
- Scalp massage to increase circulation
- Volumizing hairstyles or wigs to boost confidence during treatment
Effective hair thinning treatment for females focuses not just on regrowth but also on maintaining scalp health and self-esteem.
Living With Alopecia Areata: Coping and Confidence
Being diagnosed with alopecia can feel isolating, but you’re not alone. Many individuals find empowerment through community support, dermatological care, and education.
Here are a few ways to manage emotionally:
- Talk to a therapist if you’re struggling with self-image or stress.
- Join support groups for people with alopecia—online or in person.
- Experiment with style: wigs, scarves, and hats offer creative ways to express yourself.
Remember, hair does not define your worth. Whether you’re pursuing treatment or embracing your look, confidence comes from within.
Final Thoughts
Alopecia may be unpredictable, but it’s also manageable. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking the right treatment early can make a big difference. Whether you’re dealing with alopecia areata, alopecia barbae, or general hair thinning, options are available to help restore not just hair—but also confidence and quality of life.
If you’re noticing unusual shedding or patchy hair loss, consult a dermatologist to determine the best course of action. With the right approach, regrowth and healing are possible.