Introduction
Ulcers are painful sores that can form in various parts of the body, most commonly in the stomach and mouth. They occur when the protective lining of the tissue breaks down, allowing digestive acids or infections to create open wounds. Stomach ulcers, also called peptic ulcers or gastric ulcers, are among the most widespread digestive disorders globally. Mouth ulcers, meanwhile, are more common but generally less dangerous.
Understanding what causes a stomach ulcer, identifying symptoms early, and seeking appropriate treatment can help avoid serious complications.
This detailed guide covers ulcer causes, symptoms, treatments, risk factors, prevention, diagnosis, and tests—especially focusing on treatment for stomach ulcer and woman ulcer symptoms, as women often experience variations in signs and risk exposure.
What Is a Stomach Ulcer?
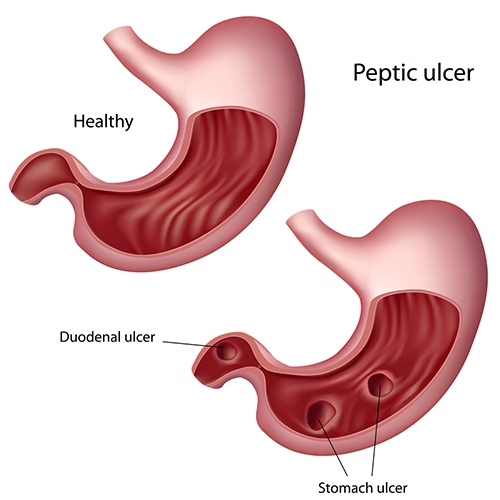
A stomach ulcer is a sore that forms on the inner lining of the stomach. When ulcers occur in the small intestine, especially the duodenum, they are called duodenal ulcers. Together, they are classified as peptic ulcer disease (PUD).
These ulcers develop when stomach acid erodes the protective lining, leading to irritation and inflammation. Without treatment, ulcers can worsen and lead to bleeding, perforation, and infection.
Types of Ulcers
There are several types of ulcers, depending on the affected body part:
Peptic Ulcers
Includes:
- Gastric ulcers: in the stomach
- Duodenal ulcers: in the upper small intestine
- Esophageal ulcers: in the food pipe
Mouth Ulcers (Canker Sores)
Common, small painful sores inside the mouth. Linked to stress, injury, and nutritional deficiencies.
Other Ulcers
- Venous leg ulcers
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Pressure ulcers (bedsores)
This article focuses primarily on stomach ulcers and mouth ulcers.
Ulcer Causes: What Causes a Stomach Ulcer?
The primary causes of stomach ulcers include:
-
Helicobacter Pylori (H. pylori) Infection
A bacteria that damages the stomach lining. It is the leading cause of peptic ulcers worldwide.
-
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Medications such as:
- Ibuprofen
- Aspirin
- Naproxen
These reduce the stomach’s protective mucus, making it vulnerable to acid.
-
Excess Stomach Acid Production
Triggered by:
- Stress
- Smoking
- Genetics
- Certain medical conditions, such as Zollinger–Ellison syndrome
-
Alcohol and Tobacco Use
These weaken the stomach lining and slow down healing.
-
Poor Dietary Habits
Spicy foods don’t directly cause ulcers but can aggravate existing ones.
Mouth Ulcer Causes (Ulcer Mouth)
Mouth ulcers may develop due to:
- Accidental cheek or lip biting
- Stress and anxiety
- Vitamin B12, zinc, and iron deficiency
- Food allergies
- Viral infections
- Hormonal fluctuations (common in women)
Symptoms of Stomach Ulcer
Ulcer symptoms differ by location and severity. Common signs include:
- Burning stomach pain
- Bloating
- Indigestion
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Dark or bloody stools (sign of internal bleeding)
- Pain worsening on an empty stomach
Woman Ulcer Symptoms
Women may have:
- Increased nausea during menstrual cycles
- Low hemoglobin (anemia)
- Heartburn after eating small meals
- Pain radiating to the back
- Menstrual cycle disturbances due to stress-related ulcer flare-ups
Mouth Ulcer Symptoms
- Small white or yellow patch with red border
- Pain while eating, drinking, or brushing
- Swelling inside mouth
- Occasional fever (if infected)
Complications if Ulcers Are Untreated
Ulcers can cause major health issues such as:
- Internal bleeding
- Perforation (hole in stomach)
- Gastric outlet obstruction (blocked digestive tract)
- Severe infection and sepsis
- Increased risk of stomach cancer (especially with untreated H. pylori)
Diagnosis and Tests for Ulcers
Doctors may use the following tests:
For Stomach Ulcers
- Endoscopy (EGD): Direct visual check of the stomach lining
- H. pylori tests (blood, stool, breath tests)
- Upper GI X-ray
- Biopsy (if cancer is suspected)
For Mouth Ulcers
- Clinical oral examination
- Blood tests to check nutrition levels
- Swab test if infection suspected
Treatment for Stomach Ulcer
The treatment of ulcer depends on the cause:
-
Antibiotics (for H. pylori)
A combination therapy called triple therapy:
- 2 antibiotics + 1 acid reducer
Usually for 10–14 days.
-
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Ulcer tablets that reduce acid production, such as:
- Omeprazole
- Pantoprazole
- Esomeprazole
-
H2-Blockers
Medications like Ranitidine or Famotidine to reduce acid formation.
-
Antacids
Relieve pain but do not heal ulcers.
-
Mucosal Protective Agents
Example: Sucralfate
Protects the ulcer from stomach acid while healing.
-
Lifestyle Modifications
- Quit smoking
- Reduce alcohol
- Healthy diet
- Stress management
Severe cases may require endoscopic treatment or surgery.
Treatment for Mouth Ulcer
Options include:
- Topical gels, ointments, or antiseptic mouthwash
- Vitamin supplements
- Pain-relief sprays
- Avoiding spicy or acidic foods
- Hydration and oral hygiene
If ulcers persist beyond 2 weeks, medical evaluation is necessary.
Diet Tips for Ulcer Management
Recommended:
- High-fiber foods
- Probiotics (curd, yogurt)
- Bananas, apples, oats
- Lean proteins
Avoid:
- Spicy and acidic foods
- Excess caffeine
- Carbonated beverages
- Fried or processed foods
Prevention: How to Reduce Ulcer Risk
- Limit NSAID use
- Manage stress
- Treat H. pylori infections promptly
- Avoid smoking and heavy alcohol use
- Practice good oral hygiene (for mouth ulcers)
- Consume a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate help if you have:
- Vomiting blood or coffee-ground-like material
- Severe abdominal pain
- Sudden weight loss
- Persistent mouth ulcers
- Black or tarry stools
Early diagnosis improves outcomes significantly.
Conclusion
Ulcers are common but treatable conditions. Understanding ulcer causes helps you take preventive action and seek timely care. Whether dealing with stomach ulcers or ulcer mouth, effective treatment exists. Paying attention to symptoms, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following medical guidance are essential for long-term digestive and oral health.
If you suspect an ulcer or have symptoms that don’t improve, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of ulcer.