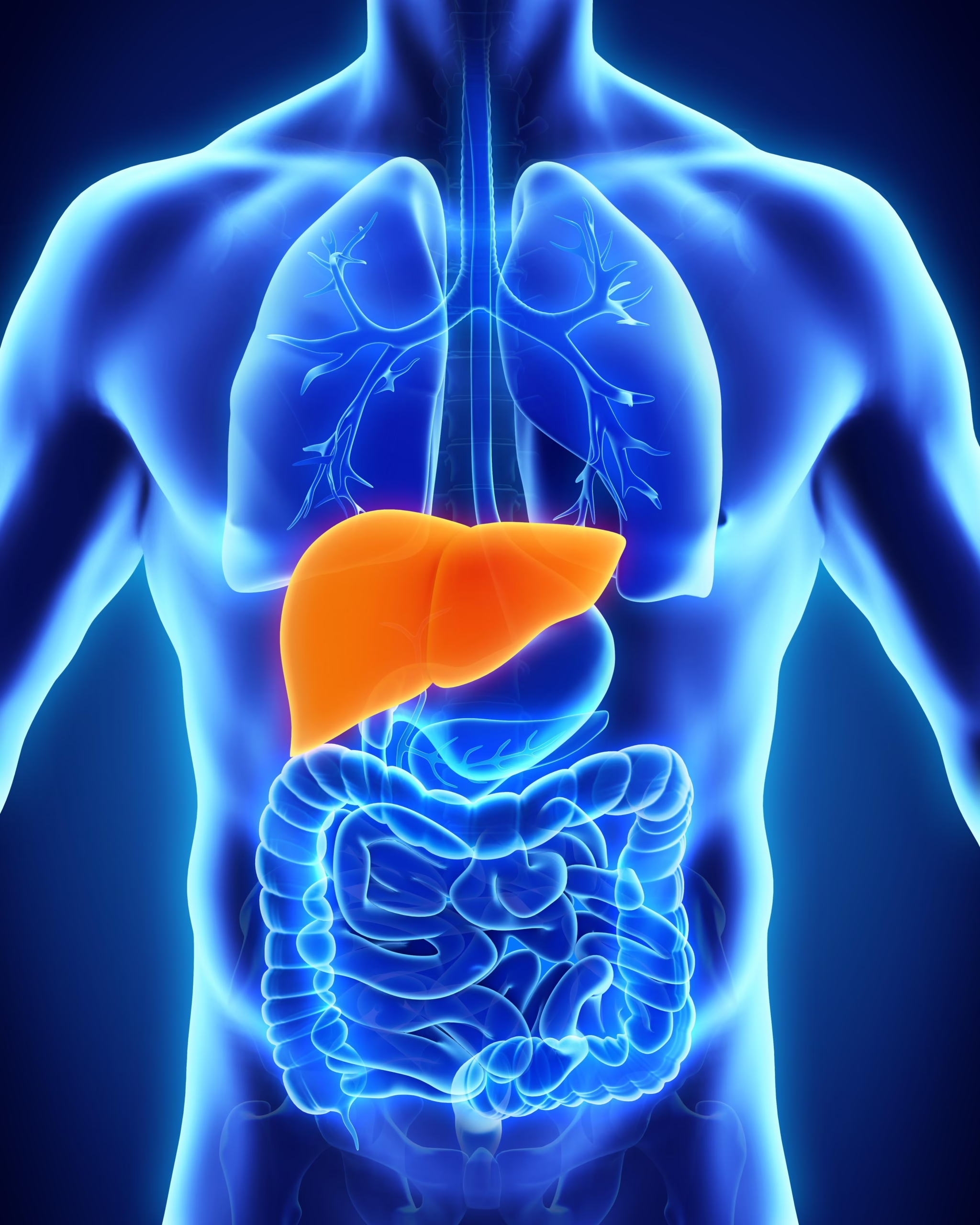
The liver is one of the most vital organs in the human body. It filters toxins, processes nutrients, and helps regulate metabolism. But when it becomes damaged, the consequences can be serious. Liver disease is a broad term that covers several conditions affecting the liver, from infections to genetic disorders to lifestyle-related issues.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know—liver disease symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis, treatments, and even which liver disease foods to avoid or eat to support recovery.
What is Liver Disease?
Liver disease refers to any condition that damages the liver and prevents it from functioning properly. Because the liver plays such a key role in detoxification and nutrient absorption, even small impairments can cause health problems throughout the body.
The liver diseases list is long and includes:
- Hepatitis (viral infection of the liver)
- Fatty liver disease (alcoholic and nonalcoholic)
- Cirrhosis (scarring of the liver)
- Liver cancer
- Genetic disorders like Hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease
- Autoimmune liver disease
In medical coding, these are often classified under liver disease ICD 10 codes for accurate documentation and insurance purposes.
Liver Disease Symptoms
Liver disease is often called a “silent illness” because many people don’t notice signs until the condition has progressed. Still, there are some common liver disease symptoms to watch for:
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Dark urine and pale stool
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss
- Liver disease and itching (pruritus due to bile salt buildup in the skin)
- Easy bruising and bleeding
- Confusion, memory problems, or difficulty concentrating
If you experience several of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical evaluation.
Causes of Liver Disease
Liver disease can develop due to a variety of factors:
- Infections – Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E) is a major cause.
- Lifestyle Choices – Excessive alcohol use, high-fat diet, and obesity can lead to fatty liver disease.
- Genetics – Conditions like Hemochromatosis (iron overload) or Wilson’s disease (copper buildup).
- Autoimmune Disorders – The immune system attacks liver cells.
- Cancer and Tumors – Liver cancer may arise from long-term cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis.
- Medications and Toxins – Overuse of drugs like acetaminophen, or exposure to harmful chemicals.
Types of Liver Disease
The liver diseases list can be grouped into major types:
- Infectious Liver Diseases: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E.
- Metabolic Liver Diseases: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), alcoholic liver disease.
- Chronic Liver Diseases: Cirrhosis, liver fibrosis.
- Cancerous Liver Diseases: Hepatocellular carcinoma, bile duct cancer.
- Genetic Disorders: Hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
- Autoimmune Liver Diseases: Autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis.
Risk Factors for Liver Disease
Certain conditions and habits increase the risk of developing liver problems:
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Unprotected sex (risk of hepatitis B and C)
- Intravenous drug use (shared needles)
- Family history of liver conditions
- Type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol
- Long-term medication use (over-the-counter painkillers, steroids)
Diagnosis and Tests for Liver Disease
Doctors use a combination of history, examination, and diagnostic tools to detect liver disease. Common tests include:
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests (ALT, AST, ALP, bilirubin) to check enzyme and toxin levels.
- Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize liver size, scarring, and tumors.
- Liver Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken to confirm diagnosis.
- FibroScan: Measures liver stiffness to check for fibrosis or cirrhosis.
These tests help determine the severity of damage and guide liver disease treatment.
Liver Disease Treatment
Treatment depends on the type and stage of liver disease. Common approaches include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Limiting alcohol, maintaining healthy weight, regular exercise.
- Medications: Antiviral drugs for hepatitis, steroids for autoimmune conditions, or chelating agents for genetic disorders.
- Surgery or Transplant: Advanced cirrhosis or liver cancer may require surgical intervention or liver transplant.
- Symptom Management: For example, antihistamines may help with liver disease and itching.
Early treatment is critical—liver damage can progress silently until it becomes irreversible.
Diet for Liver Disease: Foods to Avoid and Foods to Eat
Nutrition plays a huge role in managing liver health.
Liver Disease Foods to Avoid:
- Alcohol (worsens scarring and inflammation)
- High-fat fried foods
- Processed foods high in sugar and salt
- Red meat (hard to digest for weakened livers)
- Carbonated sugary drinks
Liver Disease Foods to Eat:
- Leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables (rich in antioxidants)
- Whole grains like oats and quinoa
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines – high in omega-3s)
- Fresh fruits (berries, apples, citrus)
- Green tea (supports detoxification)
- Nuts and seeds (healthy fats for liver function)
Adopting a liver-friendly diet is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to support recovery.
Prevention of Liver Disease
While not every case can be prevented, many risk factors are controllable.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption.
- Eat a balanced, low-fat diet.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Avoid sharing needles or personal items.
- Practice safe sex.
- Regularly monitor liver health if you have diabetes, high cholesterol, or a family history of liver disease.
Final Thoughts
The liver is the body’s natural detox powerhouse, but once damaged, it struggles to regenerate. Recognizing liver disease symptoms, getting timely tests, and making lifestyle changes are essential to managing and preventing severe complications. With the right liver disease treatment, proper diet, and consistent prevention strategies, you can safeguard your liver health for years to come.