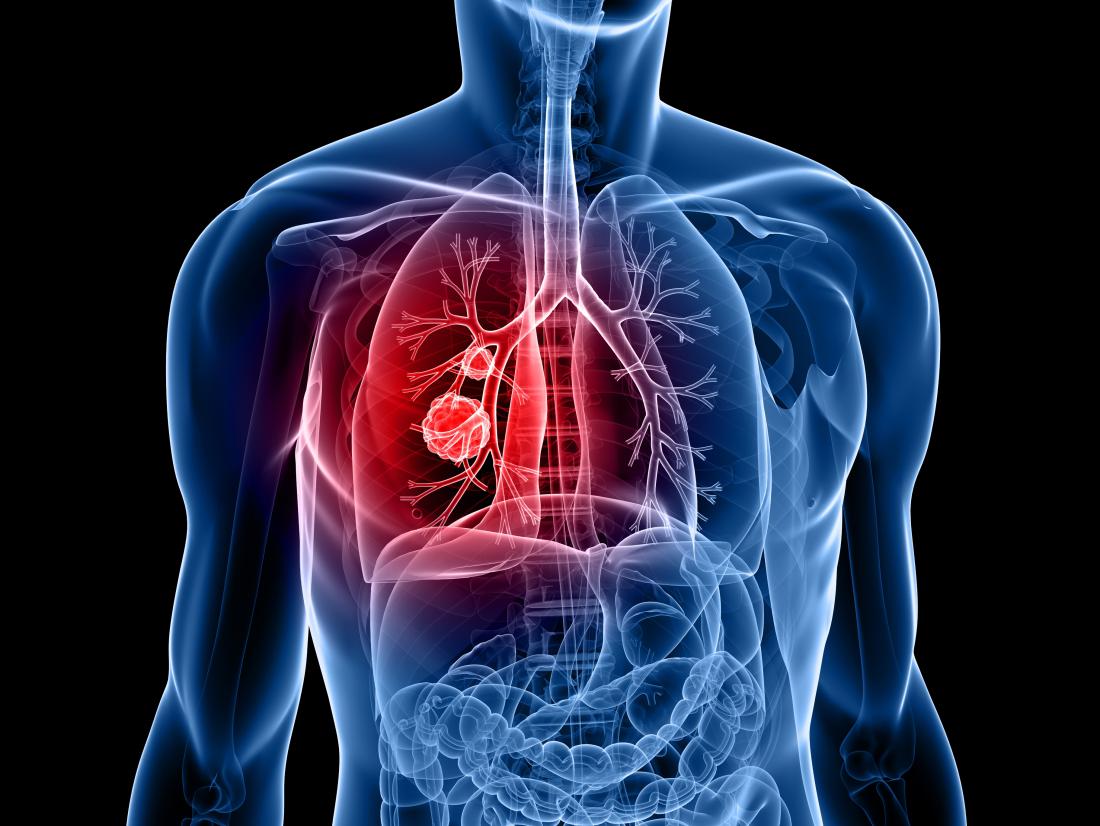
Cancer is a life-threatening health issue that affects people of all ages. It denotes abnormal growth and spreading of cells across the body. Usually, our body cells die at a certain stage after their complete growth. However, in the case of cancer patients, cells are produced enormously before the existing ones die. This overcrowding of cells in the blood leads to abnormal functions of the organs. Cancer is a tumor (solid form) that forms anywhere in the body. There are various types of cancers like breast cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, blood cancer, and so on. In this article, we are going to discuss lung cancer disease in detail.
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that affects the lungs. The body’s cells in the lungs multiply uncontrollably. In the US, lung cancer is the third common cancer that causes death. These mainly lead to shortness of breath. It affects anyone but people who have the habit of smoking or having continuous exposure to smoke, exposure to chemicals in the workplace, etc. are likely to develop the disease in common.
Types of Lung Cancer Disease
Depending on the size of the cells as seen under a microscope, lung cancer can be differentiated into two types namely,
Small cell lung cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
This is a type of pulmonary malignancy that affects both smokers and non-smokers. In non-small cell lung cancer, the malignant (cancer) cells are formed in the tissues of the lung. Depending on the types of cancer cells (as seen under a microscope), this disease is further classified into three types:
Adenocarcinoma – in this condition, cells that line the alveoli will become cancerous. They form substances called mucus all over the lung.
Large cell carcinoma – As the name implies, it mainly affects the large cells of the lung.
Squamous cell carcinoma – This type is also called epidermoid carcinoma, it begins in the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the lungs.
Who Are Vulnerable To Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma?
Anybody who smokes or has continuous exposure to smoke is at high risk of developing pulmonary cancer.
Long exposure to arsenic, asbestos, beryllium, chromium, nickel, tar, etc. in the workplace will also make anyone a lung cancer patient.
People who have gone under radiation therapy to treat other types of cancer like breast are likely to be vulnerable.
Having a family history of lung cancer disease can also develop lately.
Symptoms of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
People with lung carcinoma do not show any symptoms until they reach the last stage. However, some common complaints include:
Shortness of breath
Wheezing
A cough that gets worse over time
Chest pain
Hoarseness in the voice
Sudden weight loss
Blood in vomit
Feeling extremely fatigue
Inflammation in the veins in the neck
How to Diagnose Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The examination can be carried out by using various test methods like
- Imaging tests (CT Scan, X-Ray)
- Understanding the lifestyle to check smoker/non-smoker or exposure to toxins & chemicals, etc.
- Sputum cytology – in which a sample of mucus is examined under a microscope to check for malignant cells.
- Thoracentesis – in which a needle is used to take a fluid sample of the lining of the chest and the lung. This fluid is then examined microscopically for cancer cells.
Stages of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Once the lung cancer is diagnosed, the staging of the cancer is identified by your doctor. The stages are described based on their severity and how far it’s been spread and affected other parts.
Hidden or Occult stage – This stage cannot be identified through imaging tests or bronchoscopy. However, cancer cells can be seen in mucus or a sample taken from the airways of the lungs.
Stage 0 – here the cancer cells are seen in the lining of the airways then it is called Stage 0.
Stage 1 – If a lung tumor is identified and it is under 4cm and not yet spread to other parts then it is called Stage 1.
Stage 2 – If the cancer cells have spread to nearby tissues and lymph nodes and the tumor size is under 7cm, then you are likely to be in Stage 2.
Stage 3 – The cancer cells are spread throughout the lymph nodes and other parts surrounded by.
Stage 4 – This is life-threatening, it means the cancer cells begun to affect bones and brain, i.e. distant body parts.
Treatment Options for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Standard treatment options available to treat non-small cell lung cancer are as follows:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Laser therapy
- Cryosurgery
- Electrocautery
- Photodynamic therapy
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Small cell lung cancer is a type of lung malignancy in which cancer cells are formed in the tissues of the lungs. There are two types as follows:
- Small cell carcinoma
- Combined small cell carcinoma
Who Are At Risk, Symptoms and What Are The Treatment Options?
Like we discussed in brief for the previous type, people who are smokers or non-smokers, those who have long exposure to chemicals or toxins in the workplace, those who have undergone radiation therapy are vulnerable.
Similarly, the treatment options are common for both types of cancers.
Symptoms also remain the same for any type of lung cancer.
Stages of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Small cell lung cancer has two different stages as follows:
Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer – as the name implies, in limited-stage, the cancer cells are present only inside the lung or spread only to the lymph node.
Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer – as the name implies, the cancer cells are spread beyond the lungs or the lymph nodes.
Small cell lung cancer is recurring in patients who just recovered. It mostly affected the chest, brain, or other parts of the body.
The treatment options available these days have side effects like hair loss, so talk to your doctor in detail. Similarly, discuss the survival rate before proceeding.
Final Thoughts
The lung cancer information provided here is based on my studies and researches. It is a must to talk to your doctor, in case you doubt having the symptoms. Early-stage treatments have produced complete recovery from lung cancer. Do not panic; keep your mind calm and positive to come over this fatal disease with your doctor’s help successfully.