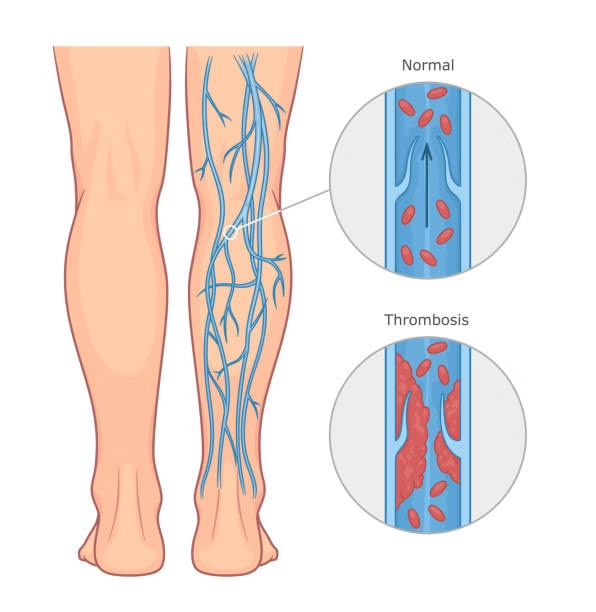
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the lower limb. It is a form of venous thrombotic disease and can become life-threatening if the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Although it is often associated with prolonged immobility or long-distance travel, deep vein thrombosis can affect individuals across various age groups and health backgrounds. Early recognition, proper diagnosis, and timely intervention significantly reduce complications.
This comprehensive guide explains:
- What deep vein thrombosis is
- Causes and underlying mechanisms
- Symptoms to watch for
- Risk factors
- Diagnosis and tests
- Treatment options
- Prevention strategies
What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis, often referred to as DVT, occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein. The most common location is the leg, especially the calf or thigh, though clots may also develop in the pelvis or arms.
When the clot forms in the lower limb, it may be described as:
- DVT in leg
- Blood clots in calf
- Blood clotting in thigh
- Large blood clot in leg
The major danger arises when part of the clot dislodges and travels through the bloodstream to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. This complication can impair oxygen exchange and may be fatal if not treated promptly.
DVT Pathophysiology: How Clots Form
Understanding DVT pathophysiology helps clarify why this condition develops.
The process of vein thrombosis is often explained by Virchow’s triad, which includes three major contributing factors:
- Venous stasis
- Endothelial injury
- Hypercoagulability
-
Venous Stasis
Venous stasis occurs when blood flow slows down. This commonly happens during:
- Prolonged bed rest
- Long flights or car rides
- Post-surgical recovery
When blood flow slows, clotting factors accumulate, increasing the likelihood of clot formation.
-
Endothelial Injury
Damage to the inner lining of the vein can trigger clot formation. This may result from:
- Trauma
- Surgery
- Inflammation
- Intravenous catheters
-
Hypercoagulability
Certain conditions increase the tendency of blood to clot. These include:
- Genetic clotting disorders
- Cancer
- Hormonal therapy
- Pregnancy
- Dehydration
When these factors combine, a thrombus may form inside the deep vein.
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis
The exact cause may vary from person to person, but common triggers include:
- Prolonged immobility
- Recent surgery
- Trauma to the leg
- Cancer and chemotherapy
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Birth control pills
- Pregnancy and postpartum period
- Obesity
- Smoking
In some cases, no obvious cause is identified. This is referred to as unprovoked DVT.
Symptoms of DVT
Symptoms may range from mild to severe. In some individuals, DVT may present without noticeable symptoms.
Common signs include:
- Swelling in one leg
- Pain or tenderness in the calf
- Warmth over the affected area
- Red or discolored skin
- Visible surface veins
Pain from blood clots in calf is often described as cramping or soreness. When the clot is higher in the leg, symptoms may involve the thigh.
In rare cases, DVT may occur in both legs, known as DVT both legs, though unilateral presentation is more common.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Immediate medical evaluation is necessary if symptoms of DVT are accompanied by:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Rapid heartbeat
- Coughing up blood
These symptoms may indicate a pulmonary embolism, a medical emergency.
Risk Factors for DVT
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing deep vein thrombosis.
-
Age
Risk increases after age 60, although younger individuals are not immune.
-
Family History
Inherited clotting disorders significantly elevate risk.
-
Prolonged Immobilization
Long hospital stays, fractures, or paralysis increase the chance of venous stasis.
-
Obesity
Excess weight puts pressure on pelvic and leg veins.
-
Cancer
Certain cancers increase clotting tendency, as do some cancer treatments.
-
Pregnancy
Hormonal changes and pressure on pelvic veins elevate risk.
-
Previous DVT
A prior episode increases recurrence risk.
Diagnosis and Tests
Accurate diagnosis is critical. A thrombosis doctor, typically a vascular specialist or hematologist, evaluates symptoms and orders appropriate tests.
Common diagnostic methods include:
-
Physical Examination
The doctor assesses:
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Skin color changes
However, physical examination alone cannot confirm DVT.
-
D-Dimer Blood Test
This test detects fragments produced when a clot dissolves. Elevated levels suggest clotting activity but are not specific to DVT.
-
Ultrasound
Compression ultrasound is the most common and reliable test. It visualizes blood flow and identifies clots in deep veins.
-
Venography
In rare cases, contrast dye is injected into veins to visualize clots on imaging.
-
MRI or CT Scan
These may be used when clots are suspected in pelvic or abdominal veins.
DVT Treatment Options
Treatment focuses on:
- Preventing clot growth
- Preventing clot migration
- Reducing recurrence risk
- Minimizing long-term complications
-
Anticoagulant Medications
These are the cornerstone of DVT treatment. They include:
- Heparin
- Low molecular weight heparin
- Direct oral anticoagulants
- Warfarin
Anticoagulants do not dissolve existing clots but prevent new ones from forming.
-
Thrombolytic Therapy
In cases involving a large blood clot in leg or severe symptoms, clot-dissolving medications may be used. These are typically reserved for high-risk situations due to bleeding risks.
-
Inferior Vena Cava Filter
If anticoagulants cannot be used, a filter may be placed in the vena cava to prevent clots from reaching the lungs.
-
Compression Stockings
These improve circulation and help prevent post-thrombotic syndrome.
Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Without treatment, DVT may lead to serious complications.
-
Pulmonary Embolism
This occurs when a clot travels to the lungs and blocks a pulmonary artery.
-
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
Chronic symptoms may include:
- Persistent swelling
- Leg pain
- Skin discoloration
- Ulcers
Prevention Strategies
Preventing deep vein thrombosis involves reducing risk factors and improving circulation.
-
Stay Physically Active
Regular movement prevents venous stasis.
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting
During long trips:
- Stand every 1 to 2 hours
- Flex and extend ankles
- Stay hydrated
-
Maintain Healthy Weight
Weight management reduces pressure on leg veins.
-
Quit Smoking
Smoking increases clotting risk and damages blood vessels.
-
Use Compression Stockings
Especially for high-risk individuals.
-
Follow Medical Advice After Surgery
Early mobilization and preventive anticoagulants are often recommended.
DVT in Special Situations
-
DVT Both Legs
While uncommon, bilateral involvement may occur in cases of:
- Severe clotting disorders
- Extensive venous obstruction
-
Cancer-Associated Thrombosis
Cancer significantly increases risk of venous thrombotic disease.
-
Recurrent DVT
Individuals with recurrent episodes may require long-term anticoagulation.
Living After a DVT Diagnosis
Long-term management includes:
- Regular follow-up
- Medication adherence
- Monitoring for bleeding
- Lifestyle modification
Patients should work closely with their thrombosis doctor to determine duration of therapy and assess recurrence risk.
Key Takeaways
- Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition involving clot formation in deep veins.
- It most commonly affects the leg.
- Symptoms may include swelling, pain, warmth, and discoloration.
- Risk factors include immobility, surgery, cancer, pregnancy, and genetic conditions.
- Diagnosis relies on ultrasound and blood tests.
- Treatment primarily involves anticoagulants.
- Prevention focuses on movement, weight control, and risk management.
Early recognition and medical evaluation are essential to prevent complications.