There’s one thing every woman experiences yet rarely talks about openly — her menstrual cycle.
It’s a rhythm that defines a woman’s body, signaling health, fertility, and balance. But when something goes wrong, the effects ripple through every aspect of life — from energy and mood to work, sleep, and even relationships.
While society is becoming more open about women’s health, period problems still remain one of the least discussed yet most common health concerns.
So today, let’s break the silence — and dive deep into understanding the menstrual cycle, what’s normal, what’s not, and how you can manage period problems naturally and effectively.
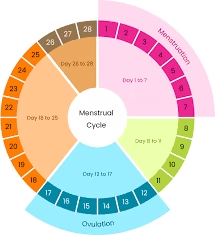
What Is the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is your body’s monthly hormonal rhythm that prepares for pregnancy.
It’s a finely tuned system controlled by a series of hormones — estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH).
A typical female menstrual cycle lasts between 21 to 35 days, but every woman’s cycle is different — and that’s completely normal.
Here’s how it works:
- Menstrual Phase (Day 1–5): The uterus sheds its lining — this is your period.
- Follicular Phase (Day 1–13): The body prepares an egg for release.
- Ovulation (Day 14): The egg is released from the ovary.
- Luteal Phase (Day 15–28): Hormones prepare the uterus for possible pregnancy.
If pregnancy doesn’t occur, hormone levels drop, triggering the next monthly period cycle.
This cycle is a powerful indicator of your overall health — which is why irregularities can signal something deeper happening in your body.
Common Period Problems Women Face
Every woman’s period story is unique. Some flow smoothly each month, while others experience discomfort, pain, or unpredictability. Let’s look at the most common period problems and what they might mean.
- Irregular Periods
When your women’s menstrual cycle doesn’t follow a consistent pattern — coming early, late, or skipping months — it’s considered irregular.
Causes include:
- Stress or anxiety
- Sudden weight changes
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
- Thyroid imbalances
- Hormonal birth control
👉 If your cycle often fluctuates beyond 35 days, it’s worth consulting your gynecologist.
- Painful Periods (Dysmenorrhea)
Cramps are common, but if you’re curled up in pain every month, it’s not normal.
Severe menstrual pain can be caused by:
- Endometriosis
- Fibroids
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Hormonal imbalance
Heat therapy, magnesium-rich foods, and gentle exercise like yoga can help relieve symptoms naturally.
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia)
If your period lasts longer than 7 days or you need to change pads every hour, you may have heavy bleeding.
Common causes:
- Uterine fibroids
- Hormone fluctuations
- Blood clotting disorders
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
Don’t ignore it — untreated heavy bleeding can cause anemia and fatigue.
- Light or Missed Periods
Sometimes periods become very light or go missing altogether (amenorrhea).
Reasons can include:
- Rapid weight loss
- Excessive exercise
- Pregnancy
- PCOS or thyroid issues
Your women period cycle is sensitive to lifestyle and hormone changes — small adjustments in nutrition and stress management can often help.
- PMS and PMDD
Mood swings, bloating, headaches, and irritability before your period? That’s PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome) — something 75% of women experience.
For some, though, it becomes more intense — leading to PMDD (Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder), a severe mood-related form of PMS.
Balancing hormones through diet, sleep, and supplements like magnesium or vitamin B6 can ease these symptoms significantly.
- Spotting Between Periods
Spotting mid-cycle can happen during ovulation or due to hormonal birth control. But frequent spotting might point to conditions like:
- Fibroids
- Polycystic ovaries
- Infections
Tracking your women menstruation pattern helps your doctor identify the cause quickly.
How Lifestyle Affects the Female Menstrual Cycle
Your hormones respond to everything — from what you eat to how you sleep. Here’s how your daily habits can shape your monthly period cycle:
Diet
A diet rich in whole foods, leafy greens, omega-3 fats, and iron supports hormonal balance.
Avoid processed foods and excess caffeine, which can worsen cramps and PMS.
Stress
Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which interfere with estrogen and progesterone — leading to irregular cycles.
Try breathing exercises, journaling, or meditation to keep your hormones steady.
Sleep
Poor sleep disrupts melatonin, which in turn affects reproductive hormones.
Aim for 7–8 hours of restful sleep to regulate your menstrual rhythm.
Exercise
Moderate exercise like walking, cycling, or yoga helps balance insulin and estrogen levels.
Over-exercising, though, can stop your period altogether — a condition known as athletic amenorrhea.
Natural Remedies for Period Problems
Modern medicine is effective, but natural remedies can complement treatment beautifully.
Here are a few evidence-backed options for menstrual support:
- Ginger: Reduces cramps and inflammation.
- Cinnamon: Balances insulin and improves menstrual flow.
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a natural hormone balancer.
- Evening Primrose Oil: Helps with PMS and breast tenderness.
- Chamomile Tea: Relaxes muscles and improves sleep.
Always consult your doctor before starting supplements — especially if you’re on medication.
Diagnosis and Tests for Menstrual Issues
When period problems persist, doctors may suggest:
- Pelvic ultrasound – to check for fibroids or cysts.
- Hormone blood tests – to assess estrogen, progesterone, thyroid, and insulin levels.
- Pap smear – to rule out infections or cervical abnormalities.
- Endometrial biopsy – if there’s unexplained heavy bleeding.
Early diagnosis helps prevent long-term complications like infertility, anemia, or endometrial disorders.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cause of your endocrine or menstrual disorder, and may include:
- Hormonal therapy: Birth control pills or progesterone to regulate cycles.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): For cramps.
- Iron supplements: For heavy bleeding-related anemia.
- Surgery: For fibroids or endometriosis in severe cases.
Alongside medical care, adopting a holistic lifestyle makes recovery smoother and long-lasting.
How to Maintain a Healthy Menstrual Cycle
Keeping your hormones balanced isn’t about perfection — it’s about consistency.
Here are some small yet powerful ways to support your female menstrual cycle naturally:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in healthy fats and fiber.
- Stay hydrated — dehydration worsens cramps.
- Track your period with an app.
- Get regular check-ups.
- Prioritize mental health — your mood and hormones are connected.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol.
When you care for your body gently, your body rewards you with balance and vitality.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical help if:
- Your periods suddenly stop for 3+ months (and you’re not pregnant).
- You bleed excessively or between periods.
- Your pain interferes with daily activities.
- You notice unusual discharge or odor.
Remember: Your menstrual cycle is a mirror of your internal health. Don’t ignore what it’s trying to tell you.
The Bottom Line
Periods are more than just a monthly inconvenience — they’re a vital sign of your health.
Understanding your women’s menstrual cycle helps you recognize what’s normal and what’s not.
If you’re facing irregular periods, pain, or mood swings, know this — you’re not alone, and help is available.
Through the right balance of lifestyle, nutrition, and medical care, you can manage period problems effectively and reclaim your comfort, confidence, and well-being.
Your body deserves your attention — every month, every cycle. ❤️